Drawing Angles In Standard Position
ANGLES IN STANDARD POSITION
An angle is said to be in standard position, if it is drawn in the xy-plane with its vertex at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x-axis.
Examples of angles in standard position :
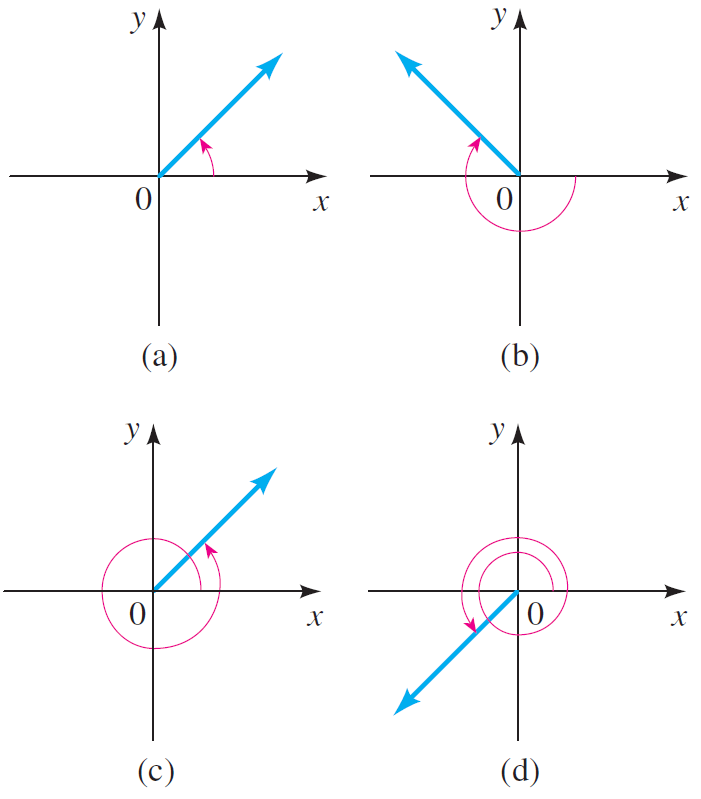
Coterminal Angles
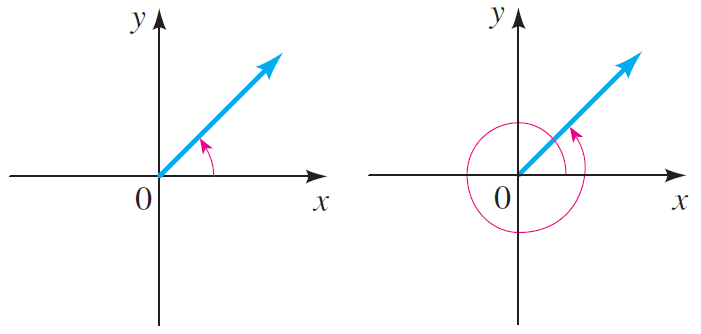
Two angles in standard position are coterminal if their sides coincide.
The two angles shown below are coterminal. Because their terminal sides coincide.
An angle is said to be in the first quadrant, if in the standard position, its terminal side falls in the first quadrant.
Similarly, we can define for the other three quadrants.
Angles in standard position having their terminal sides along the x-axis or y-axis are called quadrantal angles.
Thus, 0°, 90°, 180°, 270° and 360° are quadrantal angles.
The degree measurement of a quadrantal angle is a multiple of 90°.
Division of Quadrants
(9 0 ° - θ) -------> I st Quadrant
(90° + θ) and (18 0 ° - θ) -------> II nd Quadrant
(180° + θ) and (270° - θ) -------> III rd Quadrant
(270° + θ), (360° - θ) and ( - θ) -------> IV th Quadrant
More clearly,
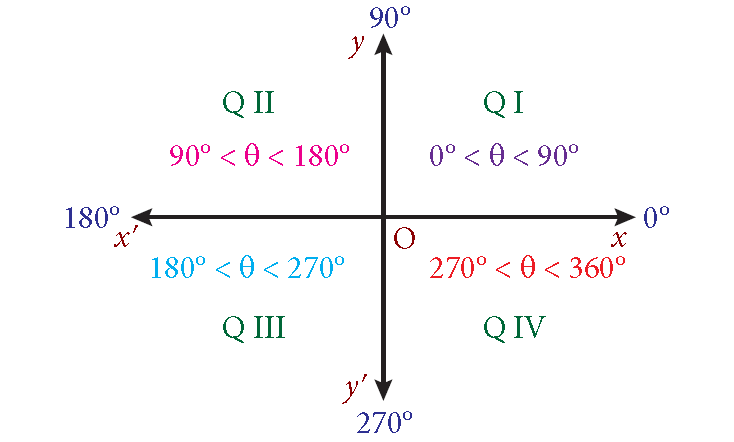
ASTC Rule
The trigonometric ratios sinθ, cosθ, tanθ, cscθ, secθ and cotθ will have different signs (positive or negative) based the quadrant where the the terminal side of the angle θ falls.
It can be easily remembered by ASTC rule.
This is nothing but "all sin tan cos" rule in trigonometry.
The "all sin tan cos" rule can be remembered easily using the following phrases.
All Sliver Tea Cups
or
All Students Take Calculus
ASTC formula has been explained clearly in the figure shown below.
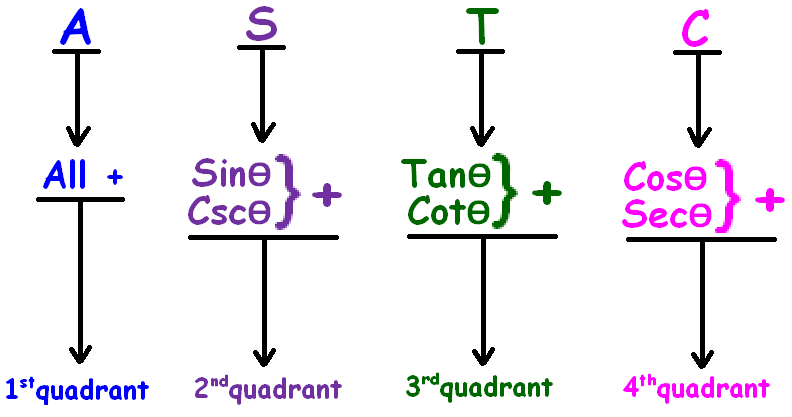
More clearly,
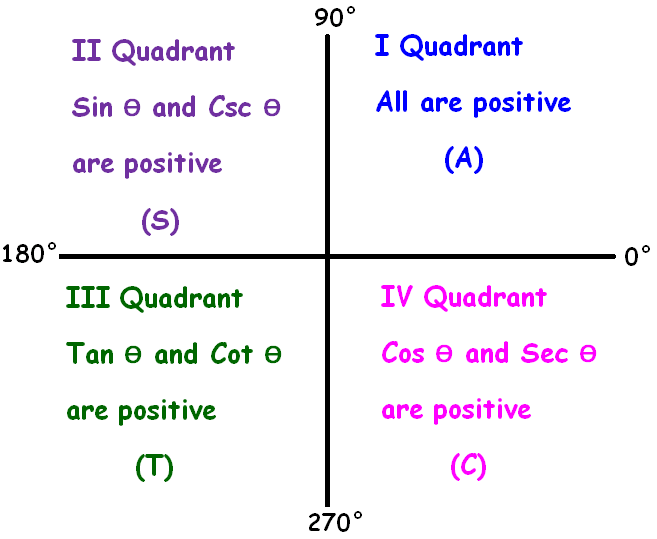
In the first quadrant (0° to 90 °), all trigonometric ratios are positive.
In the second quadrant (90° to 180 °), sin and csc are positive and other trigonometric ratios are negative.
In the third quadrant (180° to 270°), tan and cot are positive and other trigonometric ratios are negative.
In the fourth quadrant (270° to 360°), cos and sec are positive and other trigonometric ratios are negative.
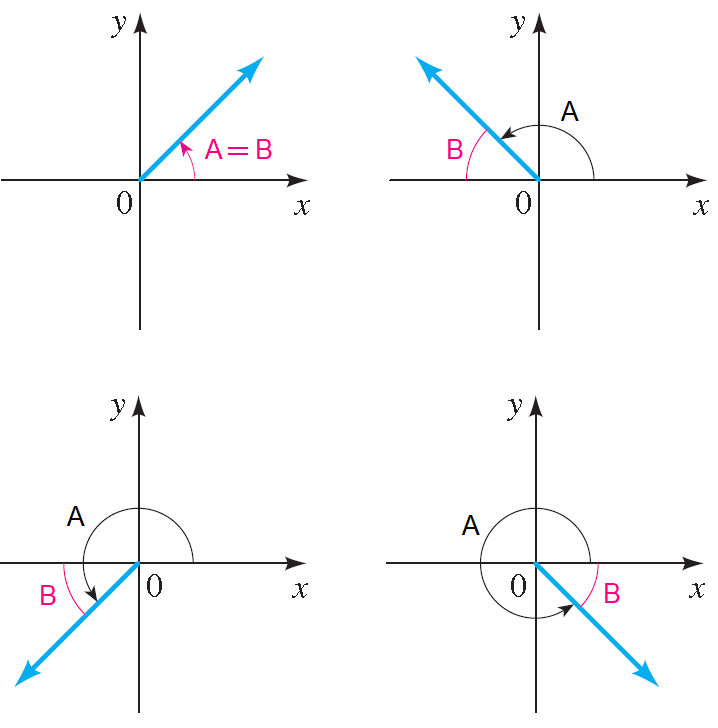
Reference Angle
Let A be an angle in standard position. The reference angle B associated with A is the acute angle formed by the terminal side of A and the x-axis.
Example :
Find the reference angle forθ = 240 °.
Solution :
The angle 240 ° has its terminal side in quadrant III, as shown below.
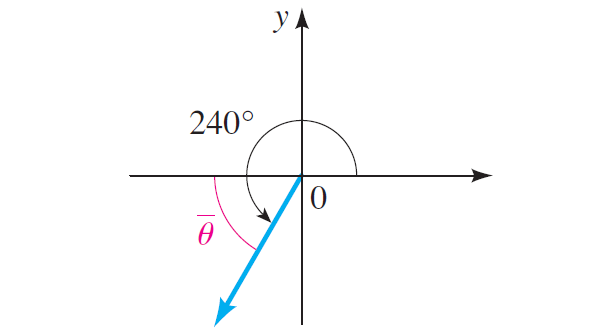
The reference angle is therefore
240 ° - 180 ° = 60 °

Apart from the stuff given above, if you need any other stuff in math, please use our google custom search here.
If you have any feedback about our math content, please mail us :
v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
You can also visit the following web pages on different stuff in math.
WORD PROBLEMS
HCF and LCM word problems
Word problems on simple equations
Word problems on linear equations
Word problems on quadratic equations
Algebra word problems
Word problems on trains
Area and perimeter word problems
Word problems on direct variation and inverse variation
Word problems on unit price
Word problems on unit rate
Word problems on comparing rates
Converting customary units word problems
Converting metric units word problems
Word problems on simple interest
Word problems on compound interest
Word problems on types of angles
Complementary and supplementary angles word problems
Double facts word problems
Trigonometry word problems
Percentage word problems
Profit and loss word problems
Markup and markdown word problems
Decimal word problems
Word problems on fractions
Word problems on mixed fractrions
One step equation word problems
Linear inequalities word problems
Ratio and proportion word problems
Time and work word problems
Word problems on sets and venn diagrams
Word problems on ages
Pythagorean theorem word problems
Percent of a number word problems
Word problems on constant speed
Word problems on average speed
Word problems on sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 degree
OTHER TOPICS
Profit and loss shortcuts
Percentage shortcuts
Times table shortcuts
Time, speed and distance shortcuts
Ratio and proportion shortcuts
Domain and range of rational functions
Domain and range of rational functions with holes
Graphing rational functions
Graphing rational functions with holes
Converting repeating decimals in to fractions
Decimal representation of rational numbers
Finding square root using long division
L.C.M method to solve time and work problems
Translating the word problems in to algebraic expressions
Remainder when 2 power 256 is divided by 17
Remainder when 17 power 23 is divided by 16
Sum of all three digit numbers divisible by 6
Sum of all three digit numbers divisible by 7
Sum of all three digit numbers divisible by 8
Sum of all three digit numbers formed using 1, 3, 4
Sum of all three four digit numbers formed with non zero digits
Sum of all three four digit numbers formed using 0, 1, 2, 3
Sum of all three four digit numbers formed using 1, 2, 5, 6
Drawing Angles In Standard Position
Source: https://www.onlinemath4all.com/angles-in-standard-position.html
Posted by: brownthisees.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Drawing Angles In Standard Position"
Post a Comment